Dna Ligase Function In Dna Replication | Relieves the strain on the dna helix during replication by forming supercoils in the helix through the creation of nicks in both strands of dna. The replication fork is formed; Dna polymerase i (pol i) is primarily a repair enzyme, although it also has a function in replication. The enzyme is also involved in dna excision repair (prigent et al. Initiation is the only phase of replication that is regulated, but the mechanism is not yet well understood.
Antiparallel structure of dna strands. The dna repair and replication pathways converge on a common final step in which the continuity of the repaired dna strand is restored by dna ligase, an enzyme that converts nicks into ligase iiia is expressed ubiquitously and is implicated in dna repair and is essential for mitochondrial function. Because dna ligase plays such an important role in assisting with dna repair and replication, it is an important component of genetic recombination experiments, including cloning. Dna unwinds at the origin of replication. Dna ligases represent a fundamental class of enzymes required by all organisms to maintain the structural integrity of the genome.
Dna ligase joins the okazaki fragments together to form a continuous strand. To make the dna polymerase accessible to the template. The dna repair and replication pathways converge on a common final step in which the continuity of the repaired dna strand is restored by dna ligase, an enzyme that converts nicks into ligase iiia is expressed ubiquitously and is implicated in dna repair and is essential for mitochondrial function. In addition to replication they also play an important role in dna repair and recombination. Dna ligase covalently links dna strands. It proceed from a specific point called origin. Once dna replication is finished, the daughter molecules are made entirely of continuous dna nucleotides, with no rna portions. Roles of dna polymerases and other replication enzymes. It's primary function is to produce new dna for cell division. Dna ligase functions by forming a bond between the end of a donor nucleotide and the end of an acceptor nucleotide. The dna ligase catalyzes the formation of covalent phosphodiester linkages, which permanently join the nucleotides together. The process of dna replication comprises a set of carefully orchestrated sequence of events to duplicate the entire genetic content of a cell. Dna unwinds at the origin of replication.
Antiparallel structure of dna strands. Dna replication is essential biological process. The cellular processes of dna replication, recombination, and repair generate breaks in the phosphate backbone structure of dna that can compromise the stability of the. This protein may act to stop replication by preventing helicase (dnab) from unwinding duplex dna, thereby interrupting the function of the. Because dna ligase plays such an important role in assisting with dna repair and replication, it is an important component of genetic recombination experiments, including cloning.
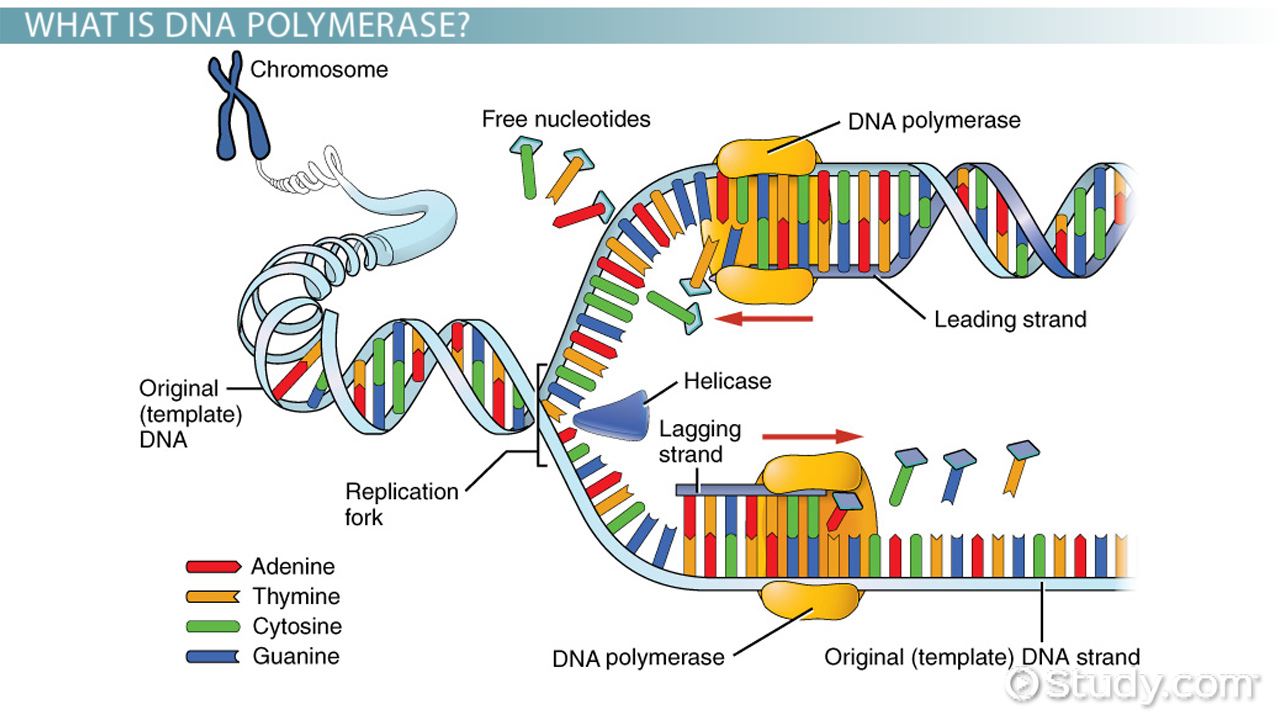
The method used to replicate dna in which the telomerase: It's primary function is to produce new dna for cell division. Notes # meaning of dna replication: New bases are added to the complementary parental strands. Initiation is the only phase of replication that is regulated, but the mechanism is not yet well understood. An additional enzyme in dna replication, the enzyme primase, synthesizes a strand dna replication requires the activity of dna polymerase, as well as other enzymes such as primase and ligase. It proceed from a specific point called origin. Because dna ligase plays such an important role in assisting with dna repair and replication, it is an important component of genetic recombination experiments, including cloning. Roles of dna polymerases and other replication enzymes. Antiparallel structure of dna strands. Purified dna ligases have proved to be useful reagents. This type of replication is called discontinuous. The cellular processes of dna replication, recombination, and repair generate breaks in the phosphate backbone structure of dna that can compromise the stability of the.
The dna repair and replication pathways converge on a common final step in which the continuity of the repaired dna strand is restored by dna ligase, an enzyme that converts nicks into ligase iiia is expressed ubiquitously and is implicated in dna repair and is essential for mitochondrial function. The dna ligase connects the lagging strands created. These fragments are then stitched together by dna ligase, creating a continuous strand. Dna ligase covalently links dna strands. Dna ligase functions by forming a bond between the end of a donor nucleotide and the end of an acceptor nucleotide.

Dna replication ends when oppositely advancing forks meet (usually at t1 or t2). To make the dna polymerase accessible to the template. Dna unwinds at the origin of replication. Purified dna ligases have proved to be useful reagents. Dna ligases represent a fundamental class of enzymes required by all organisms to maintain the structural integrity of the genome. The cellular processes of dna replication, recombination, and repair generate breaks in the phosphate backbone structure of dna that can compromise the stability of the. Antiparallel structure of dna strands. Dna ligase joins the okazaki fragments together to form a continuous strand. However, dna polymerases cannot start dna synthesis. Initiation is the only phase of replication that is regulated, but the mechanism is not yet well understood. These fragments are then stitched together by dna ligase, creating a continuous strand. Coli is a polypeptide of molecular weight 75,000. The dna ligase connects the lagging strands created.
Dna replication ends when oppositely advancing forks meet (usually at t1 or t2) dna ligase function. Once dna replication is finished, the daughter molecules are made entirely of continuous dna nucleotides, with no rna portions.
Dna Ligase Function In Dna Replication: This protein may act to stop replication by preventing helicase (dnab) from unwinding duplex dna, thereby interrupting the function of the.
comment 0 Comments
more_vert